| Previous | Contents | Index |
The LOCK class record contains data describing the operation of the lock management subsystem. The LOCK class record has a record type of 7 and a size of 56 bytes.
Figure H-19 illustrates the format of the LOCK class record.
Figure H-19 LOCK Class Record Format
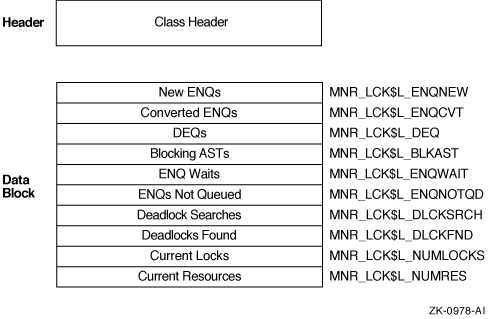
The following table describes the fields in the data block for the LOCK class record:
| Field | Symbolic Offset | Contents |
|---|---|---|
| New ENQs | MNR_LCK$L_ENQNEW | Count of new ENQ (lock) requests (longword,C) |
| Converted ENQs | MNR_LCK$L_ENQCVT | Count of converted ENQ (lock) requests (longword,C) |
| DEQs | MNR_LCK$L_DEQ | Count of DEQ (unlock) requests (longword,C) |
| Blocking ASTs | MNR_LCK$L_BLKAST | Count of blocking ASTs queued (longword,C) |
| ENQ Waits | MNR_LCK$L_ENQWAIT | Count of times a lock could not be granted immediately and waited (longword,C) |
| ENQs Not Queued | MNR_LCK$L_ENQNOTQD | Count of times a lock could not be granted immediately and got an error status instead of waiting (longword,C) |
| Deadlock Searches | MNR_LCK$L_DLCKSRCH | Count of times that a deadlock search was performed (longword,C) |
| Deadlocks Found | MNR_LCK$L_DLCKFND | Count of times that a deadlock was found (longword,C) |
| Current Locks | MNR_LCK$L_NUMLOCKS | Number of locks currently in the system (longword,L) |
| Current Resources | MNR_LCK$L_NUMRES | Number of resources currently in the system (longword,L) |
The MODES class record contains data describing time spent in each of the processor modes. The MODES class record has a record type of 2; its size depends on the number of active CPUs on the system being monitored. The size, in bytes, is calculated by adding the size of the class header, the class prefix, and the data blocks contained in the record. This is shown in the following formula, which assumes that all CPUs are active:
16 + 8 + (36 * MNR_SYI$B_MPCPUS) |
Figure H-20 illustrates the format of the MODES class record.
Figure H-20 MODES Class Record Format
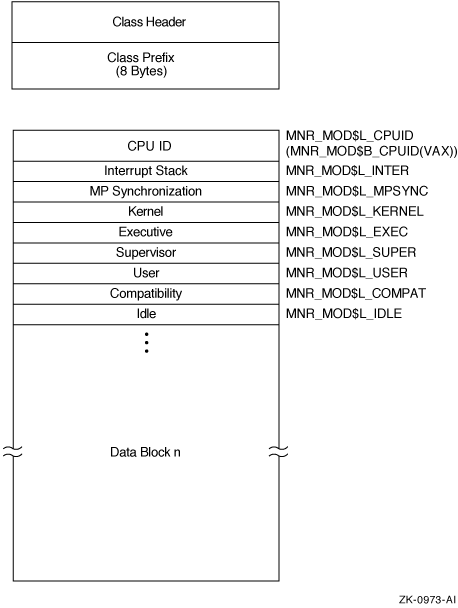
The following table describes the fields in the data block for the MODES class record:
| Field | Symbolic Offset | Contents |
|---|---|---|
| CPU ID |
MNR_MOD$L_CPUID
MNR_MOD$B_CPUID (VAX) |
CPU identification (longword,I) |
| Interrupt Stack | MNR_MOD$L_INTER | Count of clock ticks (10-millisecond units) spent on interrupt stack since system was booted (longword,C) |
| MP Synchronization | MNR_MOD$L_MPSYNC | Count of clock ticks spent synchronizing multiple CPUs since system boot |
| Kernel | MNR_MOD$L_KERNEL | Count of clock ticks spent in kernel mode, excluding interrupt stack time, since system boot (longword,C) |
| Executive | MNR_MOD$L_EXEC | Count of clock ticks spent in executive mode since system boot (longword,C) |
| Supervisor | MNR_MOD$L_SUPER | Count of clock ticks spent in supervisor mode since system boot (longword,C) |
| User | MNR_MOD$L_USER | Count of clock ticks spent in user mode, excluding compatibility mode time since system boot (longword,C) |
| Compatibility | MNR_MOD$L_COMPAT | Count of clock ticks boot spent in compatibility mode since system boot (longword,C) |
| Idle | MNR_MOD$L_IDLE | Count of clock ticks spent executing the NULL process since system boot (longword,C) |
The MSCP_SERVER class record contains data describing activities of the MSCP server. The MSCP_SERVER class record has a record type of 21 and a size of 68 bytes.
Figure H-21 illustrates the format of the MSCP_SERVER class record.
Figure H-21 MSCP_SERVER Class Record Format
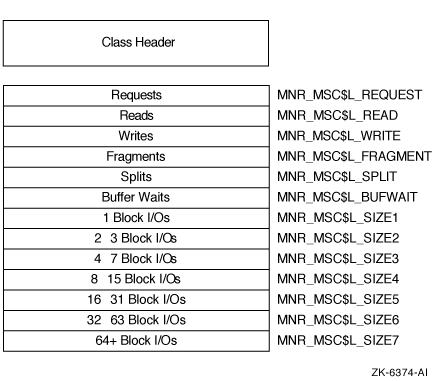
The following table describes the fields in the data block for the MSCP_SERVER class record:
| Field | Symbolic Offset | Contents |
|---|---|---|
| Requests | MNR_MSC$L_REQUEST | Count of requests for I/O transfers by remote processors (longword,C) |
| Reads | MNR_MSC$L_READ | Count of requests for Read I/O transfers by remote processors (longword,C) |
| Writes | MNR_MSC$L_WRITE | Count of requests for Write I/O transfers by remote processors (longword,C) |
| Fragments | MNR_MSC$L_FRAGMENT | Count of extra fragments issued by the server (longword,C) |
| Splits | MNR_MSC$L_SPLIT | Count of fragmented requests issued by the server (longword,C) |
| Buffer Waits | MNR_MSC$L_BUFWAIT | Count of requests that had to wait for MSCP buffer memory (longword,C) |
| 1 Block I/Os | MNR_MSC$L_SIZE1 | Count of I/O requests with a length of one block (longword,C) |
| 2---3 Block I/Os | MNR_MSC$L_SIZE2 | Count of I/O requests with a length of 2 to 3 blocks (longword,C) |
| 4---7 Block I/Os | MNR_MSC$L_SIZE3 | Count of I/O requests with a length of 4 to 7 blocks (longword,C) |
| 8---15 Block I/Os | MNR_MSC$L_SIZE4 | Count of I/O requests with a length of 8 to 15 blocks (longword,C) |
| 16---31 Block I/Os | MNR_MSC$L_SIZE5 | Count of I/O requests with a length of 16 to 31 blocks (longword,C) |
| 32---63 Block I/Os | MNR_MSC$L_SIZE6 | Count of I/O requests with a length of 32 to 63 blocks (longword,C) |
| 64+ Block I/Os | MNR_MSC$L_SIZE7 | Count of I/O requests with a length equal to or greater than 64 blocks (longword,C) |
The PAGE class record contains data describing the operation of the page management subsystem. The PAGE class record has a record type of 3 and a size of 68 bytes.
Figure H-22 illustrates the format of the PAGE class record.
Figure H-22 PAGE Class Record Format
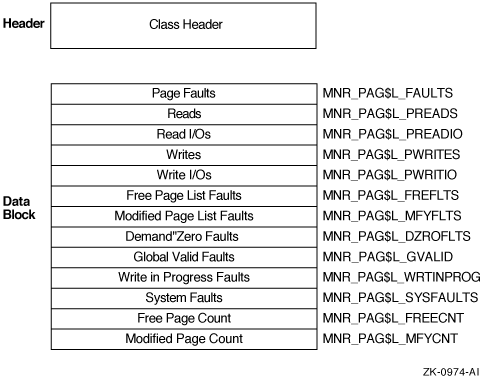
The following table describes the fields in the data block for the PAGE class record:
| Field | Symbolic Offset | Contents |
|---|---|---|
| Page Faults | MNR_PAG$L_FAULTS | Count of page faults for all working set (longword,C) |
| Reads | MNR_PAG$L_PREADS | Count of pages read from disk as a result of page faults (longword,C) |
| Read I/Os | MNR_PAG$L_PREADIO | Count of read I/Os as a result of operations from disk page faults (longword,C) |
| Writes | MNR_PAG$L_PWRITES | Count of pages written to the page file (longword,C) |
| Write I/Os | MNR_PAG$L_PWRITIO | Count of write I/O operations to the page file (longword,C) |
|
Free-page
List Faults |
MNR_PAG$L_FREFLTS | Count of pages read from the free list as a result of page faults (longword,C) |
|
Modified-page
List Faults |
MNR_PAG$L_MFYFLTS | Count of pages read from the modified list as a result of page faults (longword,C) |
|
Demand-zero
Faults |
MNR_PAG$L_DZROFLTS | Count of zero-filled pages allocated as a result of faults (longword,C) |
|
Global Valid
Faults |
MNR_PAG$L_GVALID | Count of page faults for which the reference page was found to be valid in the system global page tables (longword,C) |
|
Write-in-Progress
Faults |
MNR_PAG$L_WRTINPROG | Count of pages read that were in the process of being written back to disk when faulted (longword,C) |
| System Faults | MNR_PAG$L_SYSFAULTS | Count of page faults for which the referenced page is in system space (longword,C) |
| Free-page Count | MNR_PAG$L_FREECNT | Number of pages currently on free-page list (longword,L) |
|
Modified-page
Count |
MNR_PAG$L_MFYCNT | Number of pages currently on modified-page list (longword,L) |
The PROCESSES class record contains data describing all processes in the system. The PROCESSES class record has a record type of 0; its size depends on the number of processes being monitored. The size, in bytes, is calculated by adding the size of the class header, the class prefix, and the data blocks contained in the record. This is shown in the following formulas:
13 + 8 + (67 * the value of MNR_CMP$L_ELTCT) in OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.3-2
16 + 8 + (72 * the value of MNR_CMP$L_ELTCT) in OpenVMS Alpha Version 8.2
and I64 Version 8.2-1
16 + 8 + (96 * the value of MNR_CMP$L_ELTCT) in OpenVMS Alpha and I64
Version 8.3
|
Figure H-23 illustrates the format of the PROCESSES class record on Alpha and I64 systems.
Figure H-23 PROCESSES Class Record Format - Alpha and I64
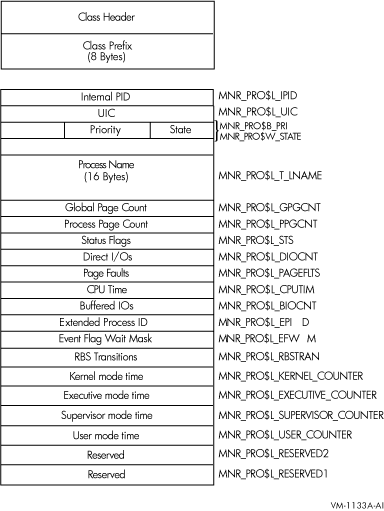
Figure H-24 illustrates the format of the PROCESSES class record on VAX systems.
Figure H-24 PROCESSES Class Record Format - VAX Only
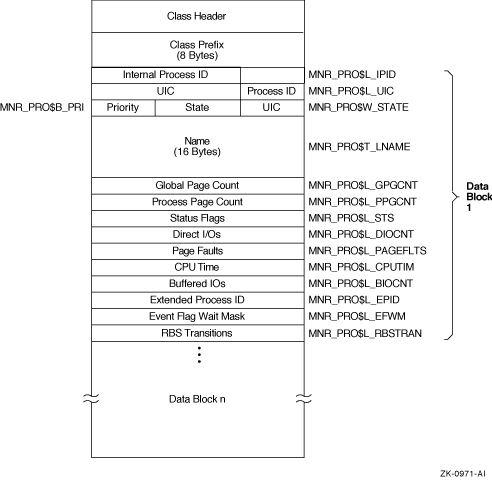
The following table describes the fields in the data block for the PROCESSES class record:
| Field | Symbolic Offset | Contents |
|---|---|---|
| Internal Process ID | MNR_PRO$L_IPID | Internal process identification (longword,I) |
| UIC | MNR_PRO$L_UIC | User identification code (Group is high-order word; Member is low-order word) (longword,I) |
| State | MNR_PRO$W_STATE | Current scheduling state code (word,I) |
| Priority | MNR_PRO$B_PRI | Current software priority (complement of 31) (byte,I) |
| Name | MNR_PRO$T_LNAME | Process name (counted ASCII string) (16 bytes,I) |
| Global Page Count | MNR_PRO$L_GPGCNT | Current global page count (longword,L) |
| Process Page Count | MNR_PRO$L_PPGCNT | Current process page count (longword,L) |
| Status Flags | MNR_PRO$L_STS | Software process status flags (PCB$V_RES bit clear implies swapped out) (longword,I) |
| Direct I/Os | MNR_PRO$L_DIOCNT | Direct I/O count (0 if swapped out) (longword,C) |
| Page Faults | MNR_PRO$L_PAGEFLTS | Page fault count (0 if swapped out) (longword,C) |
| CPU Time | MNR_PRO$L_CPUTIM | Accumulated CPU time, in 10 ms ticks (0 if swapped out) (longword,C) |
| Buffered I/Os | MNR_PRO$L_BIOCNT | Buffered I/O count (0 if swapped out) (longword,C) |
| Extended Process ID | MNR_PRO$L_EPID | Extended process identification (longword,I) |
| Event Flag Weight Mask | MNR_PRO$L_EFWM | Event flag wait mask (used for MWAITs) (longword, I) |
| RBS Transitions | MNR_PRO$L_RBSTRAN | Real balance slot transitions (longword, C) |
| Kernel mode time | MNR_PRO$L_KERNEL_COUNTER | Accumulated kernel mode, in 10-ms ticks |
| Executive mode time | MNR_PRO$L_EXECUTIVE_COUNTER | Accumulated executive mode, in 10-ms ticks |
| Supervisor mode time | MNR_PRO$L_SUPERVISOR_COUNTER | Accumulated supervisor mode, in 10-ms ticks |
| User mode time | MNR_PRO$L_USER_COUNTER | Accumulated user mode, in 10-ms ticks |
| Reserved | MNR_PRO$L_RESERVED1 | Reserved for HP internal use |
| Reserved | MNR_PRO$L_RESERVED2 | Reserved for HP internal use |
The RLOCK class record contains data that is useful for monitoring the dynamic lock remastering statistics of a node. The RLOCK class record has a record type of 27 and a size of 44 bytes.
Figure H-25 illustrates the format of the RLOCK class record.
Figure H-25 RLOCK Class Record Format
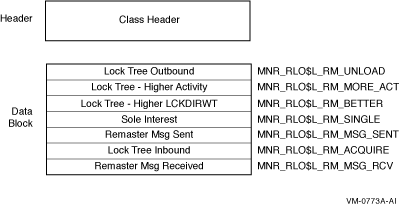
The following table describes the fields in the data block for the RLOCK class record:
| Field | Symbolic Offset | Contents |
|---|---|---|
| Lock Tree Outbound | MNR_RLO$L_RM_UNLOAD | Count of lock trees that are moved from this node. |
| Lock Tree-Higher Activity | MNR_RLO$L_RM_MORE_ACT | Count of trees that are moved due to higher locking activity on another node in the cluster. |
| Lock Tree-Higher LCKDIRWT | MNR_RLO$L_RM_BETTER | Count of trees that are moved to a node with a higher value of the system parameter LCKDIRWT. |
| Sole Interest | MNR_RLO$L_RM_SINGLE | Count of trees that are moved to another node because that node is the only one with locks remaining on the tree. |
| Remaster Msg Sent | MNR_RLO$L_RM_MSG_SENT | Count of remaster messages sent from this node. |
| Lock Tree Inbound | MNR_RLO$L_RM_ACQUIRE | Count of trees that are moved to this node. |
| Remaster Msg Received | MNR_RLO$L_RM_MSG_RCV | Count of remaster messages received on this node. |
The RMS class record contains data describing Record Management Services for specified files. The RMS class record has a record type of 20. Use the following formula to calculate the record size (the formula calculates the size by adding the size of the class header, the class prefix, and the data blocks contained in the record):
16 + 8 + (276 * MNR_CMP$L_ELTCT) |
Figure H-26 illustrates the format of the RMS class record.
Figure H-26 RMS Class Record Format
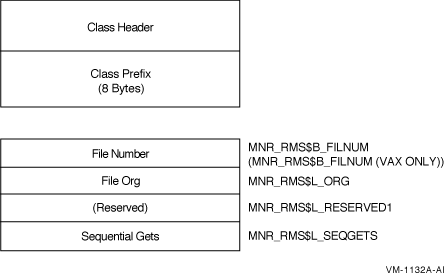
The following table describes the fields in the data block for the RMS class record:
| Field | Symbolic Offset | Contents |
|---|---|---|
| File Number (Num) |
MNR_RMS$L_FILNUM
MNR_RMS$B_FILNUM (VAX) |
Sequential number of the file (byte,I) |
| File Organization | MNR_RMS$L_ORG | Organization of the file (longword,I) |
| Reserved | MNR_RMS$L_RESERVED1 | Reserved (longword) |
| Sequential GETs | MNR_RMS$L_SEQGETS | Count of sequential $GETs to the file (longword,C) |
The SCS class record contains data describing SCS (System Communications Services) activity for all SCS connections in the system, on a per-node basis. The SCS class record has a record type of 15; its size depends on the number of nodes being monitored. The size, in bytes, is calculated by adding the size of the class header, the class prefix, and the data blocks contained in the record. This is shown in the following formula:
16 + 8 + (56 * the value of MNR_CMP$L_ELTCT) |
Figure H-27 illustrates the format of the SCS class record.
Figure H-27 SCS Class Record Format
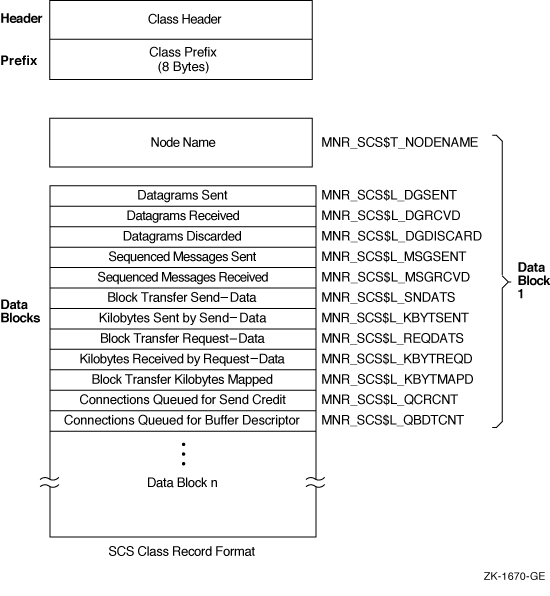
The following table describes the fields in the data block for the SCS class record:
| Field | Symbolic Offset | Contents |
|---|---|---|
| Node Name | MNR_SCS$T_NODENAME | Name of remote cluster node (counted ASCII string) (8 bytes,I) |
| Datagrams Sent | MNR_SCS$L_DGSENT | Count of datagrams sent to the remote node (longword,C) |
| Datagrams Received | MNR_SCS$L_DGRCVD | Count of datagrams received from the remote node (longword,C) |
| Datagrams Discarded | MNR_SCS$L_DGDISCARD | Count of datagrams discarded by the CI port driver (longword,C) |
| Sequenced Messages Sent | MNR_SCS$L_MSGSENT | Count of sequenced messages sent to the remode node (longword,C) |
| Seqenced Messages Received | MNR_SCS$L_MSGRCVD | Count of sequenced messages received from the remote node (longword,C) |
|
Block Transfer
Send-data commands |
MNR_SCS$L_SNDATS | Count of block transfer send-data commands initiated on the local node, targeted for the remote node (longword,C) |
|
Kilobytes Sent by
Send-data commands |
MNR_SCS$L_KBYTSENT | Count of kilobytes sent as a result of send-data commands (longword,C) |
|
Block Transfer Request-
data commands |
MNR_SCS$L_REQDATS | Count of block transfer request-data commands initiated on the local node, targeted for the remote node (longword,C) |
|
Kilobytes Received by
Request-data commands |
MNR_SCS$L_KBYTREQD | Count of kilobytes received as a result of request-data commands (longword,C) |
|
Block Transfer
Kilobytes Mapped |
MNR_SCS$L_KBYTMAPD | Count of kilobytes mapped for block transfers (longword,C) |
|
Connections Queued For
Send Credit |
MNR_SCS$L_QCRCNT | Count of times connections are queued for send credits (longword,C) |
|
Connections Queued For
Buffer Descriptor |
MNR_SCS$L_QBDTCNT | Count of times connections are queued for buffer descriptors (longword,C) |
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index |