| Previous | Contents | Index |
Converts an absolute 128-bit binary time into its numeric components. The numeric components are returned in local time.On Alpha and I64 systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
SYS$NUMUTC timbuf ,[utcadr]
int sys$numutc (unsigned short int timbuf [13], unsigned int *utcadr [4]);
timbuf
OpenVMS usage: vector_word_unsigned type: word access: write only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha and I64); by 32-bit reference (VAX)
Buffer into which $NUMUTC writes the converted date and time. The timbuf argument is the 32-bit address (on VAX systems) or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha and I64 systems) of a 13-word structure containing time, inaccuracy of time, and time differential factor. The time differential factor encoded in the 128-bit buffer is used to convert the UTC to its numerical components. Negative values in the inaccuracy field indicate an infinite inaccuracy.The following diagram depicts the fields in this structure:
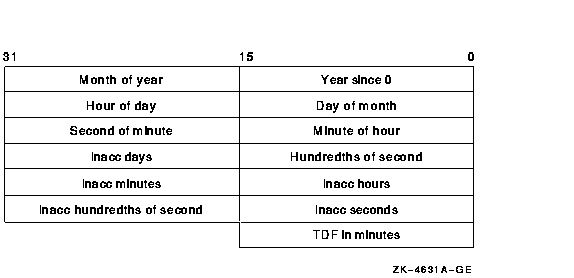
| OpenVMS usage: | coordinated universal time |
| type: | utc_date_time |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha and I64); by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
The utcadr argument is optional; if it is not used, $NUMUTC will use the current time.
SS$_NORMAL The service completed successfully. SS$_INVTIME The 128-bit UTC time is not valid.
The Next Volume service allows you to process the next tape volume in a multiple volume set. This service applies only to files on magnetic tape volumes.For additional information about this service, see the OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
The Open service makes an existing file available for processing by your program. The Open service specifies the type of record access to be used and determines whether the file can be shared. The Open service also performs an implicit Display service.For additional information about this service, see the OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
The Parse service analyzes the file specification string and fills in various NAM block fields.For additional information about this service, see the OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
Parses the specified text string and converts it to the binary representation for an access control entry (ACE).
SYS$PARSE_ACL aclstr ,aclent ,[errpos] ,[accnam] ,[nullarg]
int sys$parse_acl (void *aclstr, void *aclent, unsigned short int *errpos, void *accnam, int (*routin)(void));
aclstr
OpenVMS usage: char_string type: character-coded text string access: read only mechanism: by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
Formatted ACE that is parsed when $PARSE_ACL completes execution. The aclstr argument is the address of a string descriptor pointing to the text string to be parsed.aclent
OpenVMS usage: char_string type: character-coded text string access: write only mechanism: by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
Description of the ACE that is parsed when $PARSE_ACL completes execution. The aclent argument is the address of a descriptor pointing to the buffer in which the ACE is written. The first byte of the buffer contains the length of the ACE; the second byte contains a value that identifies the type of ACE, which in turn defines the format of the ACE.For information about the ACE types and their associated formats, see $FORMAT_ACL system service documentation.
errpos
OpenVMS usage: word_unsigned type: word (unsigned) access: write only mechanism: by reference
Number of characters from aclstr processed by $PARSE_ACL. The errpos argument is the address of a word that receives the number of characters actually processed by the service. If the service fails, this count points to the failing point in the string.accnam
OpenVMS usage: access_bit_names type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by reference
Names of the bits in the access mask when $PARSE_ACL is executing. The accnam argument is the address of an array of 32 quadword descriptors that define the names of the bits in the access mask. Each element points to the name of a bit. The first element names bit 0, the second element names bit 1, and so on.You can call LIB$GET_ACCNAM to retrieve the access name table for the class of object whose ACL is to be formatted. If you omit accnam, the following names are used:
Bit Name Bit 0 READ Bit 1 WRITE Bit 2 EXECUTE Bit 3 DELETE Bit 4 CONTROL Bit 5 BIT_5 Bit 6 BIT_6 .
.
.Bit 31 BIT_31 nullarg
OpenVMS usage: null_arg type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Placeholding argument reserved to HP.
The Parse Access Control List Entry service parses the specified text string and converts it to the binary representation for an access control entry (ACE).None
None
$ADD_HOLDER, $ADD_IDENT, $ASCTOID, $CHECK_ACCESS, $CHKPRO, $CREATE_RDB, $ERAPAT, $FIND_HELD, $FIND_HOLDER, $FINISH_RDB, $FORMAT_ACL, $FORMAT_AUDIT, $GET_SECURITY, $GRANTID, $HASH_PASSWORD, $IDTOASC, $MOD_HOLDER, $MOD_IDENT, $MTACCESS, $REM_HOLDER, $REM_IDENT, $REVOKID, $SET_SECURITY
SS$_NORMAL The service completed successfully. SS$_ACCVIO The string or its descriptor cannot be read by the caller; the buffer descriptor cannot be read by the caller; the buffer cannot be written by the caller; or the buffer is too small to hold the ACL entry. SS$_IVACL The format of the access control list entry is not valid. SS$_NOSUCHID The specified identifier does not exist in the rights database.
On Alpha and I64 systems, disables user process alignment fault reporting.
SYS$PERM_DIS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT
int sys$perm_dis_align_fault_report (void);
None.
The Disable Alignment Fault Reporting service disables user process alignment fault reporting.See the description of the $PERM_REPORT_ALIGN_FAULT service for an example of a program that can be used to enable and disable user process alignment fault reporting.
None
None
$GET_ALIGN_FAULT_DATA, $GET_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_DATA, $INIT_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $PERM_REPORT_ALIGN_FAULT, $START_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $STOP_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $STOP_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT
SS$_NORMAL The service completed successfully.
On Alpha and I64 systems, initializes user process alignment fault reporting.
SYS$PERM_REPORT_ALIGN_FAULT
int sys$perm_report_align_fault (void);
None.
The Report Alignment Fault service allows the user to permanently enable user process alignment fault reporting for all subsequent images.This service reports alignment faults only in exception mode. For more information about reporting modes, see the $START_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT service.
Image alignment fault reporting takes precedence over process alignment fault reporting; that is, if both image and process alignment fault reporting are enabled, faults are reported to the image first.
None
None
$GET_ALIGN_FAULT_DATA, $GET_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_DATA, $INIT_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $PERM_DIS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $START_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $STOP_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT, $STOP_SYS_ALIGN_FAULT_REPORT
SS$_NORMAL The service completed successfully.
/**********************************************************************/
/* */
/* SET_ALIGN_REPORT.C */
/* */
/* This program can be used to permanently turn on and off */
/* alignment fault reporting for a process. After creating the */
/* executable, do: */
/* */
/* $ align :== $dir:set_align_report.exe */
/* $ align on */
/* $ run program ! will generate align faults on screen */
/* $ align off */
/* $ run program ! will not generate align faults */
/* */
/**********************************************************************/
#include <stdio>
#include <ctype>
#include <ssdef>
/* alignment fault reporting system services */
extern sys$perm_report_align_fault(),
sys$perm_dis_align_fault_report();
main(argc, argv)
int argc;
char *argv[];
{
int status;
/* check arguments */
if (argc < 2) {
printf ("Insufficient arguments\n");
return (40);
}
/* check if the argument is on or off */
if ((strcmp ("ON", argv[1]) == 0) || (strcmp ("on", argv[1]) == 0))
/* on, turn alignment fault reporting on for this process */
status = sys$perm_report_align_fault ();
else if ((strcmp ("OFF", argv[1]) == 0) || (strcmp ("off", argv[1]) == 0))
/* off, turn alignment fault reporting off for this process */
status = sys$perm_dis_align_fault_report ();
else
return (SS$_BADPARAM);
/* return status */
return (status);
}
|
This example shows a program that can be used to enable and disable alignment fault reporting for a process.
Modifies the context of the current process to match the context of a given persona. The $PERSONA_ASSUME service allows an OpenVMS process to assume the identity of another user or to discard a persona to return the process to its original state.
SYS$PERSONA_ASSUME persona ,[flags]
int sys$persona_assume (unsigned int *persona, unsigned int flags);
persona
OpenVMS usage: integer type: longword (unsigned) access: read mechanism: by reference
Address of a longword in which the persona identification handle is expected.If the value of the context passed is 1, then the current persona is discarded, and the state of the calling process is returned to the state that existed prior to the first call to $PERSONA_CREATE.
flags
OpenVMS usage: mask_longword type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Flag mask specifying which Persona services options are to be employed when the persona is assumed. This argument is ignored when a persona is being discarded.The following table describes each flag:
Flag Description IMP$M_ASSUME_SECURITY Assume access rights, UIC, authorized privileges, user name, and security audit flag. IMP$M_ASSUME_ACCOUNT Assume OpenVMS account. IMP$M_ASSUME_JOB_WIDE Assume the new persona, even in a multiprocess job.
When assuming a persona using the IMP$M_ASSUME_SECURITY option, any previously enabled image privileges will be disabled. The caller's process will have only the privileges of the impersonated user enabled. These privileges are enabled in the Current, Process, and Authorized privilege masks.When using IMP$M_ASSUME_SECURITY, access to the job logical name table might no longer be possible because the table is protected by the UIC of the user on whose behalf the current process was created. Also, a new access to the process' controlling terminal might fail, and the process might be in a different default resource domain for locking.
Any persona is automatically discarded and deleted upon image exit. Hence, it is not possible to permanently change the persona of a process using $PERSONA_ASSUME.
The arguments are read in caller's mode, so an invalid argument can cause an access violation to be signaled.
None
None
$PERSONA_CREATE, $PERSONA_DELETE
SS$_NORMAL The service completed successfully; the desired access is granted. IMP$_NOCHJIB The Job Information Block cannot be modified. IMP$_PERSONANONGRATA Invalid persona argument.
On Alpha and I64 systems, allows an OpenVMS thread to assume the identity of another persona.
SYS$PERSONA_ASSUME persona ,[flags], [previous], [acmode]
int sys$persona_assume (unsigned int *persona, unsigned int flags, unsigned int *previous, unsigned int acmode);
persona
OpenVMS usage: persona type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by reference
Address of a longword in which the persona identification handle is expected.If the value passed is ISS$C_ID_NATURAL, then the state of the calling thread is returned to the natural persona.
flags
OpenVMS usage: mask_longword type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Ignored.previous
OpenVMS usage: persona type: longword (unsigned) access: write only mechanism: by reference
Address of a longword into which the persona identification handle of the currently active persona being replaced is written.acmode
OpenVMS usage: access_mode type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Access mode to be considered when assuming a persona. The acmode argument is a longword containing the access mode.The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller. Only equal or more privileged access modes can use this persona.
This service establishes the specified persona as the active security profile and returns the persona identification handle of the persona that was active at the point in which the call to this service was made.On image exit, the natural persona is assumed and all nonpermanent personae are deleted.
The arguments are validated against the caller's mode, so an invalid argument can cause an access violation to be signaled.
None
None
$PERSONA_CLONE, $PERSONA_CREATE, $PERSONA_CREATE_EXTENSION, $PERSONA_DELETE_EXTENSION, $PERSONA_DELEGATE, $PERSONA_DELETE, $PERSONA_EXTENSION_LOOKUP, $PERSONA_FIND, $PERSONA_MODIFY, $PERSONA_QUERY, $PERSONA_RESERVE
SS$_NORMAL The service completed successfully; the desired access is granted. SS$_ACCVIO Access violation. SS$_INSFARG Certain required arguments were not specified. SS$_IVMODE The caller cannot create a persona that is more privileged than the caller. SS$_NOPRIV The operation requires IMPERSONATE privilege. SS$_PERSONANONGRATA Invalid persona argument.
On Alpha and I64 systems, creates a copy of an existing persona within the context of the current process. The service returns the assigned persona identification for the new persona in the persona argument. This persona can be assumed using the $PERSONA_ASSUME service.
SYS$PERSONA_CLONE persona ,[input]
int sys$persona_clone (unsigned int *persona, unsigned int *input);
persona
OpenVMS usage: persona type: longword (unsigned) access: write only mechanism: by reference
Address of a longword into which the persona identification handle is written.input
OpenVMS usage: persona type: longword (unsigned) access: write only mechanism: by reference
Address of a longword containing the persona identification of the persona to be cloned. If this argument is 0, null, or absent, the currently active persona is cloned.
The Clone Persona service creates a copy of an existing persona within the context of the current process. The service returns the assigned persona identification for the new persona in the persona argument. This persona can be assumed using the $PERSONA_ASSUME service.On image exit, the natural persona is assumed and all nonpermanent personae are deleted.
None
BYTLM
$PERSONA_ASSUME, $PERSONA_CREATE, $PERSONA_CREATE_EXTENSION, $PERSONA_DELETE_EXTENSION, $PERSONA_DELEGATE, $PERSONA_DELETE, $PERSONA_EXTENSION_LOOKUP, $PERSONA_FIND, $PERSONA_MODIFY, $PERSONA_QUERY, $PERSONA_RESERVE
SS$_NORMAL The service completed successfully. SS$_ACCVIO Access violation. SS$_EXQUOTA The caller lacks sufficient quota to allocate a new persona. SS$_INSFMEM Insufficient memory. SS$_IVMODE The caller cannot create a persona that is more privileged than the caller. SS$_PERSONANONGRATA The persona ID supplied was invalid.
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index |