| Previous | Contents | Index |
On Alpha and I64 systems, converts a binary value into an ASCII character string in decimal, hexadecimal, or octal notation; returns the character string in an output string; and inserts variable character-string data into an output string.$FAOL_64 interprets the parameter list as a list of quadwords rather than a list of longwords. In all other respects, $FAOL_64 is identical to $FAOL. For all other information about the $FAOL_64 service, refer to the description of $FAO/$FAOL in this manual.
This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
SYS$FAOL_64 ctrstr_64 [,outlen_64 [,outbuf_64 [,quad_prmlst_64]]]
int sys$faol_64 (void *ctrstr_64, unsigned short int *outlen_64, void *outbuf_64, void *quad_prmlst_64);
ctrstr_64
OpenVMS usage: char_string type: character-coded text string access: read only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
The 32- or 64-bit address of the control string (64-bit or 32-bit string descriptor).outlen_64
OpenVMS usage: word_unsigned type: word (unsigned) access: write only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference
The 32- or 64-bit address of the quadword that contains the output length, in bytes, of the fully formatted output string.outbuf_64
OpenVMS usage: char_string type: character-coded text string access: write only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
The 32- or 64-bit address of a character string descriptor that points to the output buffer into which $FAOL_64 writes the fully formatted output string.
quad_prmlst_64
OpenVMS usage: vector_quadword_unsigned type: quadword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference
The 32- or 64-bit address of a quadword-aligned array of quadword FAO arguments.
Searches a string for a file specification and parses the components of that file specification.
SYS$FILESCAN srcstr ,valuelst ,[fldflags] ,[auxout] ,[retlen]
int sys$filescan (void *srcstr, void *valuelst, unsigned int *fldflags, void *auxout, unsigned short int *retlen);
srcstr
OpenVMS usage: char_string type: character-coded text string access: read only mechanism: by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
String to be searched for the file specification. The srcstr argument is the address of a descriptor pointing to this string.valuelst
OpenVMS usage: item_list_2 type: longword (unsigned) access: modify mechanism: by reference
Item list specifying which components of the file specification are to be returned by $FILESCAN. The components are the full node specification, primary node name, primary node's access control, secondary node information, device, directory, file name, file type, and version number. The itmlst argument is the address of a list of item descriptors wherein each item descriptor specifies one component. The list of item descriptors is terminated by a longword of 0.The following diagram depicts a single item descriptor:
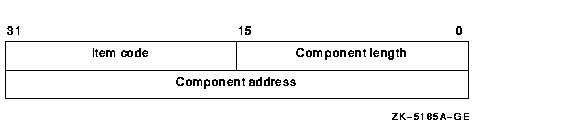
The following table defines the item descriptor fields:
| Descriptor Field | Definition |
|---|---|
| Component length | A word in which $FILESCAN writes the length (in characters) of the requested component. If $FILESCAN does not locate the component, it returns the value 0 in this field and in the component address field and returns the SS$_NORMAL condition value. |
| Item code | A user-supplied, word-length symbolic code that specifies the component desired. The $FSCNDEF macro defines the item codes. |
| Component address | A longword in which $FILESCAN writes the starting address of the component. This address points to a location in the input string itself. If $FILESCAN does not locate the component, it returns the value 0 in this field (see item code FSCN$_NAME for exception) and 0 in the component length field, and returns the SS$_NORMAL condition value. |
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
The $FSCNDEF macro defines a symbolic name for each significant flag bit. The following table shows the file specification component that corresponds to the symbolic name of each flag bit:
| Symbolic Name | Corresponding Component |
|---|---|
| FSCN$V_DEVICE | Device name |
| FSCN$V_DIRECTORY | Directory name |
| FSCN$V_NAME | File name |
| FSCN$V_NODE | Node name |
| FSCN$V_NODE_ACS | Access control string of primary node |
| FSCN$V_NODE_PRIMARY | Primary (first) node name |
| FSCN$V_NODE_SECONDARY | Secondary (additional) node information |
| FSCN$V_ROOT | Root directory name string |
| FSCN$V_TYPE | File type |
| FSCN$V_VERSION | Version number |
The fldflags argument is optional. When you want to know which components of a file specification are present in a string but do not need to know the contents or length of these components, specify fldflags instead of valuelst.
| OpenVMS usage: | char_string |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
When you specify an auxiliary output buffer, $FILESCAN copies the entire source string, with quotation information reduced and simplified for only the primary node, into the auxiliary output buffer.
When the auxiliary output buffer is provided, all addresses returned in the item list point to locations in the auxiliary output buffer.
| OpenVMS usage: | word_unsigned |
| type: | word (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
FSCN$_DEVICE
Returns the length and starting address of the device name. The device name includes the single colon (:).FSCN$_DIRECTORY
Returns the length and starting address of the directory name. The directory name includes the brackets ([ ]) or angle brackets (< >).FSCN$_FILESPEC
Returns the length and starting address of the full file specification. The full file specification contains the node, device, directory, name, type, and version.FSCN$_NAME
Returns the length and starting address of the file name. The file name includes no syntactical elements.$FILESCAN also returns the length and starting address of a quoted file specification following a node specification (as in the specification NODE::"FILE-SPEC"). The beginning and ending quotation marks are included.
If there is no name component but there is either a type or version component, the flags argument for FSCN$V_NAME is set and the address field contains a nonzero pointer (pointing to the period for the type component); however, the length field does contain zero.
FSCN$_NODE
Returns the length and starting address of the full node specification. The full node specification includes the primary node name, the primary node's access control string, any secondary node information, and the final double colon (::).FSCN$_NODE_ACS
Returns the length and starting address of the primary access control string. If multiple nodes are specified, the primary access control string represents the control information (if present) for the first node specified. The primary access control string does not contain the double colon (::), but does contain the double quotes.FSCN$_NODE_PRIMARY
Returns the length and starting address of the primary node name. If multiple nodes are specified, the primary node name represents the first node specification. The node name does not include the double colon (::) or any access control information. If an auxiliary output buffer is specified, quotation information is reduced and simplified for only the primary node.FSCN$_NODE_SECONDARY
Returns the length and starting address of any secondary node information. The secondary node string contains any node information referring to additional nodes, including the final double colon (::), as well as any access control strings (if present) for the additional nodes.FSCN$_ROOT
Returns the length and starting address of the root directory string. The root directory name string includes the brackets ([ ]) or angle brackets (< >).FSCN$_TYPE
Returns the length and starting address of the file type. The file type includes the preceding period (.).FSCN$_VERSION
Returns the length and starting address of the file version number. The file version number includes the preceding period (.) or semicolon (;) delimiter.
The Scan String for File Specification service searches a string for a file specification and parses the components of that file specification. When $FILESCAN locates a partial file specification (for example, DISK:[FOO]), it returns the length and starting address of those components that were requested in the item list and were found in the string. If a component was requested in the item list but not found in the string, $FILESCAN returns a length of 0 and an address of 0 to the component address field in the item descriptor for that component (see item code FSCB$_NAME for exception).The information returned about all of the individual components describes the entire contiguous file specification string. For example, to extract only the file name and file type from a full file specification string, you can add the length of these two components and use the address of the first component (file name). However, the specific node name and node control strings extracted using the FSCN$_NODE_PRIMARY and FSCN$_NODE_ACS item codes cannot be recombined because the double colon (::) is not included in either string.
If an auxiliary output buffer is provided, $FILESCAN copies the entire source string, removing and reducing quotation marks from the primary node name.
The $FILESCAN service does not perform comprehensive syntax checking. Specifically, it does not check that a component has a valid length.
However, $FILESCAN does check for the following information:
- The component must have required syntactical elements; for example, a directory component must be enclosed in brackets ([]), and a node name must be followed by an unquoted double colon (::).
- The component must not contain invalid characters. Invalid characters are specific to each component. For example, a comma (,) is a valid character in a directory component but not in a file type component.
- Spaces, tabs, and carriage returns are permitted within quoted strings, but are invalid anywhere else.
- If a node name contains a space, tab, double quote ("), or double colon (::), then the node name must be quoted.
The node component of a file specification contains one or more node specifications. A node specification is a node name, followed by an optional access control string, followed by a double colon (::). A node name is either a standard name or a quoted name.
If the node name contains quotation marks, the quotes must be doubled ("") and the entire node name quoted. For example, the node abc"def" would be represented as "abc""def""". An access control string is a quoted string containing a user name, an optional password, and an optional account name. Note that the double quotes are only used to differentiate between a primary node name containing embedded quotes and the access control string. See the Example section for the proper use of this syntax.
Invalid characters are treated as terminators. For example, if $FILESCAN encounters a space within a file name component, it assumes that the space terminates the full file specification string.
For node names, a space, tab, double quote ("), and comma (,) are treated as terminators and must be quoted if they are part of the node name. In addition, the double colon (::) and the trailing colon (for example, NODE:) are treated as terminators and must also be quoted if they are part of the node name.
The $FILESCAN service recognizes the DEC Multinational alphabetical characters (such as à) as alphanumeric characters.
The $FILESCAN service accepts extended (ODS-5) file names. The parsing types and names are independent of the volume they reside on; therefore, if the device name points to an ODS-2 volume, you can specify an ODS-5 file name. Refer to the Guide to OpenVMS File Applications for information on ODS-5 file specifications.
The $FILESCAN service does not (1) assume default values for unspecified file specification components, (2) perform logical name translation on components, (3) perform wildcard processing, or (4) perform directory lookups.
None
None
$ALLOC, $ASSIGN, $BRKTHRU, $BRKTHRUW, $CANCEL, $CREMBX, $DALLOC, $DASSGN, $DELMBX, $DEVICE_SCAN, $DISMOU, $GETDVI, $GETDVIW, $GETMSG, $GETQUI, $GETQUIW, $INIT_VOL, $MOUNT, $PUTMSG, $QIO, $QIOW, $SNDERR, $SNDJBC, $SNDJBCW, $SNDOPR
SS$_NORMAL The service completed successfully. SS$_ACCVIO The service could not read the string pointed to by the srcstr argument; or it could not write to an item descriptor in the item list specified by the valuelst argument; or it could not write to the specified auxiliary output buffer; or the retlen argument could not be written. SS$_BADPARAM The item list contains an invalid item code.
! The following is a C example for using the $FILESCAN service.
#include <perror.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <descrip.h>
#include <iledef.h>
#include <fscndef.h>
#include <starlet.h>
#include <ssdef.h>
//
// Build table of names. Verify positions in table.
//
#if FSCN$_FILESPEC != 1
#error "table assumption for FILESPEC is invalid."
#endif
#if FSCN$_NODE_SECONDARY != 11
#error "table assumption for NODE_SECONDARY is invalid."
#endif
char *name_field[] = {
"",
"FILESPEC",
"NODE",
"DEVICE",
"ROOT",
"DIRECTORY",
"NAME",
"TYPE",
"VERSION",
"NODE_PRIMARY",
"NODE_ACS",
"NODE_SECONDARY" } ;
typedef struct fldflags FLDFLAGS ;
main(int argc, char *argv[] )
{
int status ;
int field_flags ;
char *filename;
struct dsc$descriptor_s file_name = { 0 } ;
struct dsc$descriptor_s output_string = { 0 } ;
short retlen ;
int i ;
ile2 itmlst[] = {
{0, FSCN$_FILESPEC, 0},
{0, FSCN$_NODE, 0},
{0, FSCN$_DEVICE, 0},
{0, FSCN$_ROOT, 0},
{0, FSCN$_DIRECTORY, 0},
{0, FSCN$_NAME, 0},
{0, FSCN$_TYPE, 0},
{0, FSCN$_VERSION, 0},
{0, FSCN$_NODE_PRIMARY, 0},
{0, FSCN$_NODE_ACS, 0},
{0, FSCN$_NODE_SECONDARY, 0},
{ 0, 0, 0 } } ;
output_string.dsc$w_length = 4096 ;
if ((output_string.dsc$a_pointer = malloc(4096)) == NULL) {
perror("Malloc Failure");
exit(0) ;
}
if ((file_name.dsc$a_pointer = filename = malloc(4096)) == NULL) {
perror("Malloc Failure");
exit(0) ;
}
for( ;; ) {
printf("\nEnter file name: ") ;
if (gets(filename) == NULL)
break ;
file_name.dsc$w_length = strlen(filename) ;
status = sys$filescan( &file_name, itmlst, &field_flags,
&output_string, &retlen) ;
if (!(status&1)) exit(status) ;
if ((itmlst[0].ile2$ps_bufaddr != NULL) && (retlen != 0))
printf("The file name returned is %.*s\n", retlen,
(char*)itmlst[0].ile2$ps_bufaddr ) ;
else
printf("There is no file name returned for FSCN$_FILESPEC\n");
for( i = 0; i < FSCN$_NODE_SECONDARY; i++) {
if ((int)field_flags & 1<<i)
printf("The component %s is present: %.*s\n", name_field[i+2],
itmlst[i+1].ile2$w_length,
(char*)itmlst[i+1].ile2$ps_bufaddr ) ;
}
}
exit(status) ;
}
|
This C example demonstrates the use of the $FILESCAN service.
Following is an example of the program output:
$ RUN TEST_SCAN Enter file name: abc"def" The file name is abc"def" The component NAME is present: abc Enter file name: "abc""def""" There is no file name returned for FSCN$_FILESPEC Enter file name: "abc""def""":: The file name is abc"def":: The component NODE is present: abc"def":: The component NODE_PRIMARY is present: abc"def" Enter file name: "abc""def""""user password":: The file name is abc"def""user password":: The component NODE is present: abc"def""user password":: The component NODE_PRIMARY is present: abc"def" The component NODE_ACS is present: "user password" Enter file name: abc"def":: The file name is abc"def":: The component NODE is present: abc"def":: The component NODE_PRIMARY is present: abc The component NODE_ACS is present: "def" Enter file name: "abc""def""""system password"::[dir.1]a^ ^".file;1 The file name returned is abc"def""system password"::[dir.1]a^ ^".file;1 The component NODE is present: abc"def""system password":: The component DIRECTORY is present: [dir.1] The component NAME is present: a^ ^" The component TYPE is present: .file The component VERSION is present: ;1 The component NODE_PRIMARY is present: abc"def" The component NODE_ACS is present: "system password"
The Find service locates a specified record in a file and returns its record file address in the RAB$W_RFA field of the RAB. The Find service can be used with all file organizations.For additional information about this service, see the OpenVMS Record Management Services Reference Manual.
Returns the identifiers held by a specified holder.
SYS$FIND_HELD holder ,[id] ,[attrib] ,[contxt]
int sys$find_held (struct _generic_64 *holder, unsigned int *id, unsigned int *attrib, unsigned int *contxt);
holder
OpenVMS usage: rights_holder type: quadword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by reference
Holder whose identifiers are to be found when $FIND_HELD completes execution. The holder argument is the address of a quadword data structure containing the holder identifier. This quadword data structure consists of a longword containing the holder UIC, followed by a longword containing the value 0.id
OpenVMS usage: rights_id type: longword (unsigned) access: write only mechanism: by reference
Identifier value found when $FIND_HELD completes execution. The id argument is the address of a longword containing the identifier value with which the holder is associated.attrib
OpenVMS usage: mask_longword type: longword (unsigned) access: write only mechanism: by reference
Attributes associated with the holder returned in id when $FIND_HELD completes execution. The attrib argument is the address of a longword containing a bit mask specifying the attributes.Symbol values are offsets to the bits within the longword. You can also obtain the values as masks with the appropriate bit set using the prefix KGB$M rather than KGB$V. The symbols are defined in the system macro library ($KGBDEF). The following are the symbols for each bit position:
Bit Position Meaning When Set KGB$V_DYNAMIC Allows holders of the identifier to remove it from or add it to the process rights list by using the DCL command SET RIGHTS_LIST. KGB$V_NOACCESS Makes any access rights of the identifier null and void. This attribute is intended as a modifier for a resource identifier or the Subsystem attribute. KGB$V_RESOURCE Allows the holder to charge resources, such as disk blocks, to the identifier. KGB$V_SUBSYSTEM Allows holders of the identifier to create and maintain protected subsystems by assigning the Subsystem ACE to the application images in the subsystem. contxt
OpenVMS usage: context type: longword (unsigned) access: modify mechanism: by reference
Context value used when repeatedly calling $FIND_HELD. The contxt argument is the address of a longword used while searching for all identifiers. The context value must be initialized to 0, and the resulting context of each call to $FIND_HELD must be presented to each subsequent call. After contxt is passed to $FIND_HELD, you must not modify its value.
The Find Identifiers Held by User service returns a list of the identifiers that another identifier holds. Use the $FIND_HELD service to construct the process rights when a user logs in (unless that process has read access to the rights database). To determine all the identifiers held by the specified holder, call $FIND_HELD repeatedly until it returns the status code SS$_NOSUCHID. When SS$_NOSUCHID is returned, $FIND_HELD has returned all the identifiers, cleared the context value, and deallocated the record stream.If you complete your calls to $FIND_HELD before SS$_NOSUCHID is returned, use $FINISH_RDB to clear the context value and deallocate the record stream.
Note that, when you use wildcards with this service, the records are returned in the order that they were originally written because the first record is located on the basis of the holder ID. Thus, all the target records have the same holder ID or, in other words, they have duplicate keys, which leads to retrieval in the order in which they were written.
Read access to the rights database is required to obtain information about identifiers held by other users.
None
$ADD_HOLDER, $ADD_IDENT, $ASCTOID, $CREATE_RDB, $FIND_HOLDER, $FINISH_RDB, $GRANTID, $IDTOASC, $MOD_HOLDER, $MOD_IDENT, $REM_HOLDER, $REM_IDENT, $REVOKID
SS$_NORMAL The service completed successfully. SS$_ACCVIO The id argument cannot be written by the service, or the holder, attrib, or contxt argument cannot be read by the service. SS$_IVCHAN The contents of the contxt longword are not valid. SS$_INSFMEM The process dynamic memory is insufficient for opening the rights database. SS$_IVIDENT The format of the specified holder identifier is invalid. SS$_NOIOCHAN No more rights database context streams are available. SS$_NOSUCHID The specified holder identifier does not exist, or no further identifiers are held by the specified holder. RMS$_PRV You do not have read access to the rights database.
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index |